All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Why Double-glazed Windows Are A Must in Manning Western Australia
That window can transfer more solar heat in winter than in summertime. A west-facing window on a summer season's afternoon has an angle of occurrence from near 0 up to 30 with a big reliable location of solar radiation. A north-facing window, in summer season, has a high angle of occurrence and a low reliable area of solar radiation, so can transfer less heat than a west-facing one.

You can quickly and quickly enhance the thermal efficiency of your house by replacing your windows. This is among the most effective approaches of remodelling to attain improved thermal comfort. There are thousands of kinds of glass and frames to select from. Choosing the ideal ones is essential to improving the energy efficiency of your home.
How Double Glazing Can Help Keep Your Home Cool In ... in Mount Hawthorn Perth
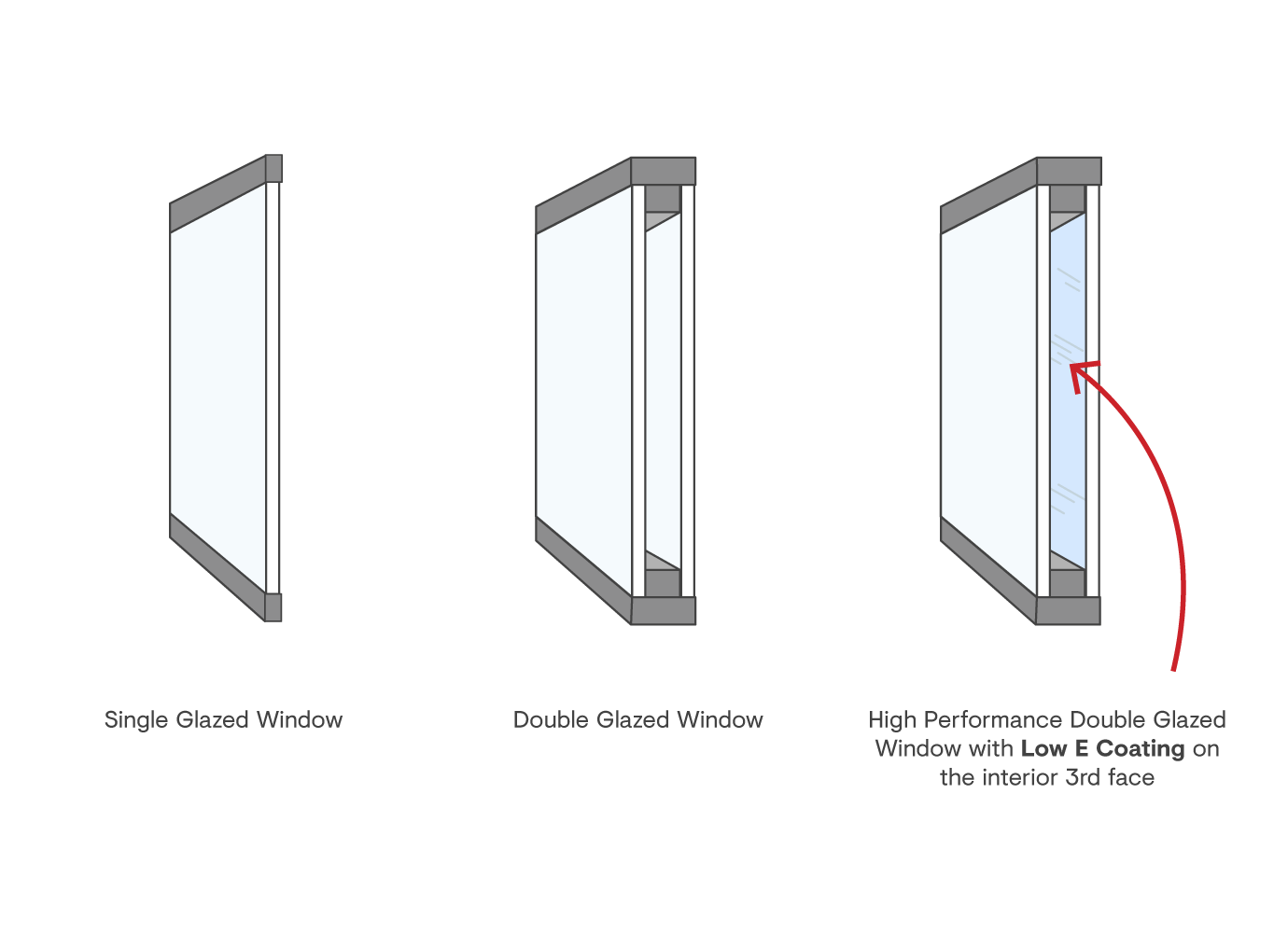
Single glazing with clear glass is not very effective when it comes to heat loss or gain. To enhance performance, you can use single glazing with a more energy-efficient type of glass such as low emissivity (low-e) glass.
The energy efficiency of IGUs likewise depends on: the residential or commercial properties of each layer of glass. Various glass types (for example, clear and low-e glass) can be put together in an IGU.
The Best Double Glazing Companies In Canberra in Middle Swan WA
IGU cavities can be filled with air or a more inert, low-conductivity gas such as argon the width of the cavity. Cavity density is normally 6 to 18mm. Wider cavities provide lower (much better) U worths, with 12mm generally accepted as the preferred space how well the cavity is sealed. Cavities need to be dry and well sealed to prevent wetness getting in.
If argon is installed to the cavity in place of air, moisture is dependably omitted the level of desiccant (drying representative). The spacer (metal or polymer strip) that separates the glass layers consists of a desiccant to soak up any moisture. Insufficient desiccant may cause moisture to condense on the glass surface area in cold conditions, decreasing thermal performance.
Top 10 Tips To Keep Your Home Cool in North Lake Western Australia
In fact, IGUs can deliver much better energy performance for all climates, specifically in heated and air-conditioned houses. Cross-section information of single, double and triple-glazing systems Low emissivity glass (frequently known as low-e glass) reduces heat transfer. Low-e glass might be either high or low transmission: High transmission low-e glass has a finishing that enables daytime from the sun to enter your house to accomplish great solar heat gain, however minimizes the quantity of the long wavelength infrared heat that can escape back through the window.
Low-e glass has either a pyrolytic finishing or a vacuum-deposited thin movie metal covering. Pyrolytic coverings are resilient and can be used for any glazing; vacuum-deposited coatings are soft and are just used within IGUs. Low-e coatings can considerably enhance both U value and SHGC; nevertheless, they should be utilized correctly or they will either deteriorate or stop working to perform as required.
Buy Double Glazed Upvc Sliding Doors In Sydney in Wattle Grove Perth
Low-e coverings can be used in combination with clear, toned or reflective glass. Low-e finishings on glazing can lower heat transfer where required Picture: Department of Market, Science, Energy and Resources Toned glass has actually colouring additives included throughout manufacture. It is available in various colours, normally bronze, grey, blue and green.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Triple Glazing Vs. Double Glazing: What Are The Differences? in North Beach Western Australia
What Are The Best Upvc Windows For Summer in Secret Harbour WA
Why Is Double Glazing So Important In Winter? in Yanchep WA
More
Latest Posts
Triple Glazing Vs. Double Glazing: What Are The Differences? in North Beach Western Australia
What Are The Best Upvc Windows For Summer in Secret Harbour WA
Why Is Double Glazing So Important In Winter? in Yanchep WA